Evolution of Ebola Virus – Where are we now? Scientists continue to study theevolution of the
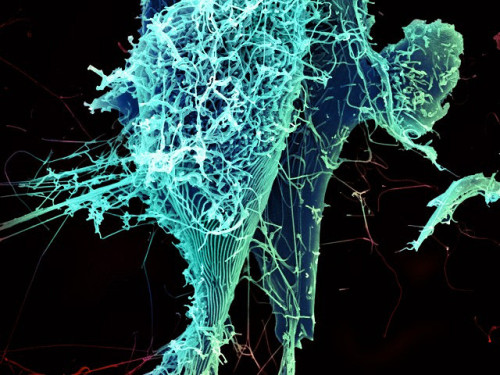
Evolution of Ebola Virus – Where are we now? Scientists continue to study theevolution of the Ebola virus following the West African outbreak to determinehow extraordinary numbers of humans became infected. Their results showed genetic changes occurring as the virustransmitted from human to human. To be sure, the theory was put to test. Researchers focused on the surfaceprotein which the virus uses to bind a protein receptor on the surface of thetarget cell in order to gain entry. After identifying genetic changes accruingin the surface protein, synthetic clones were generated to see if mutantproteins behave differently to those seen in virus samples at the start of theoutbreak.The data was clear, a number of geneticchanges that occurred during the outbreak increased infectivity. One change in particular, a substitution of an amino acidinvolved in receptor binding, was particularly striking: not simply because itdramatically increased infectivity, but also because it was present in virusesthat dominated the West African outbreak.Another twist from the study, mutations that increased infectivity inhuman cells seemed to reduce the ability of the protein to mediate entry intocells obtained from fruit bat cells - said to be the natural hostfor ebola virus.Unprecedented number of human to human transmissions gave the virus anopportunity to adapt to humans; an opportunity the virus didn’t miss.ReadmoreImages: Credit: NIAID; String-like Ebola virus particles are shedding from an infected cell in this electron micrograph. Credit: Nixxphotography; Ebola Virus Disease Credit: Credit Maurizio De Angelis, Wellcome Images; Ebola virus structure, illustration -- source link
Tumblr Blog : bbsrc.tumblr.com
#virus ebola#medical#medical research#viruses#human health#human disease#human cells#nurses#human biology#mutation#research#genetics#medicine#genetic changes#science#infection