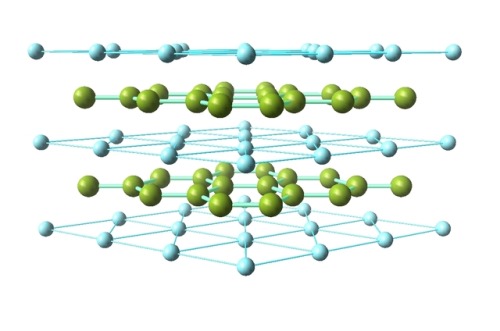
Ceramics: Magnesium diborideClassified as a simple binary compound, magnesium diboride (MgB2) is als
Ceramics: Magnesium diborideClassified as a simple binary compound, magnesium diboride (MgB2) is also sometimes known as an intermetallic superconductor. It has a hexagonal crystal structure, which forms two-dimensional layers of boron in a graphite-like structure between the triangular layers of magnesium (as seen in the two images above). MgB2‘s biggest claim to fame is its status as a relatively inexpensive superconductor. Among conventional superconductors (those that are phonon-mediated), it has one of the highest critical temperatures, at around 39 K. Though it had been known as a material to scientists for some time, its superconductivity was not discovered until 2001. Aside from being a high-temperature superconductor, MgB2 also has more than one superconducting energy gap, something theorized but rarely seen experimentally. The bulk, polycrystalline form of the material can be easily made by exposing solid boron to magnesium vapor at high temperatures. Single crystals of the material are more difficult to form, but can be done so under high pressure. Thin films are often made through hybrid physical-chemical vapor deposition. Applications (or possible applications) of MgB2 often take advantage of its superconductivity, such as in MRIs and tokamaks, but the material does have other suggested uses. The compound burns completely when ignited in oxygen, and so has been proposed for usage as a fuel in ramjets, or in blast-enhanced explosives and propellants. Sources: ( 1 - image 3 ) ( 2 ) ( 3 ) ( 4 ) ( 5 ) ( 6 )Image sources: ( 1 ) ( 2 ) ( 4 ) -- source link
Tumblr Blog : materialsscienceandengineering.tumblr.com
#materials science#science#ceramics#magnesium diboride#magnesium#superconductivity#superconductors#mymsepost#materialsposts